In medicine, the heart rate (HR) or heart rate refers to the number of cardiac actions during a certain unit of time (usually 1 minute), equivalent to bpm. It is made up of two phases that repeat rhythmically: a contraction phase (systole) and a subsequent relaxation phase (diastole). Sinus rhythm is the term used to describe the normo-frequent, regular heartbeat in humans.
During physical exertion, the heart rate increases under normal conditions. This mechanism is initially significantly influenced by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The rate also increases during deep inspiration and decreases during deep expiration. This is influenced by the sympathetic function and is referred to as respiratory arrhythmia. The constant adaptation of the heart rate to the demands of the whole organism is also referred to as heart rate variability (HRV).
The resting heart rate depends on various factors and is different for men and women (ideally measured in the morning before getting up). The following resting heart rate values should be taken as a rough guide:
ott-2024_embodied-data_berlin.pdf
https://www.cardiosecur.com/de/ihr-herz/fachartikel-rund-um-das-herz/das-gesunde-herz
The ECG is a graphical representation of the currents generated by the heartbeat. A normal ECG analysis shows a characteristic curve. This curve consists of three phases that are repeated with each pumping cycle.
https://www.ratgeber-herzinsuffizienz.de/erkennen/herzuntersuchungen/ekg
The R wave is the highest wave of the electrocardiogram, as this is where the greatest electrical activity is found. This represents the depolarization of the myocardium (heart muscles) of both ventricles, from the base of the heart to the apex.
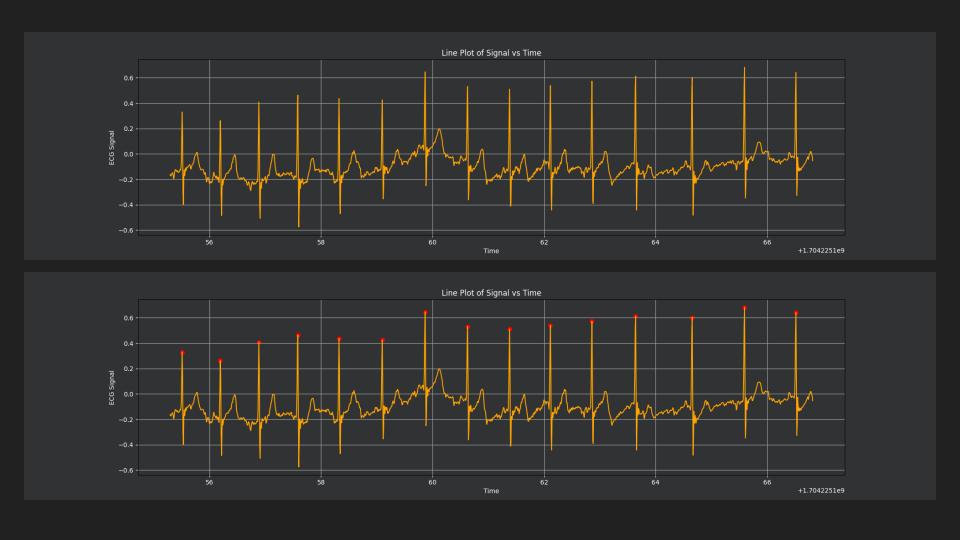 EKG mit R-Zacken, Datenvisualisierung CSV-File Aufnahme Brustgurt, Datum, Länge
EKG mit R-Zacken, Datenvisualisierung CSV-File Aufnahme Brustgurt, Datum, Länge
The RR interval is the time interval between two R-waves in the ECG and corresponds to the duration of an electrical heart action (measured in ms: milliseconds). The RR interval is slightly dependent on breathing (can fluctuate by 30 ms, for example). During inhalation, the heart speeds up and the vagus nerve is blocked; during exhalation, it slows down and the vagus nerve is stimulated. This phenomenon is called respiratory sinus arrhythmia. (Often only visible on the ECG in younger people).
The time intervals between two heartbeats are called NN intervals. They are never identical because the heart sometimes beats faster and sometimes slower, depending on a variety of factors. The heart rate during exercise is higher than that at rest. Heart rate variability is an indicator of the heart's ability to adapt to different demands. It shows how the heartbeat reacts to various internal or external factors. Heart rate variability or heart rate variability (HR variability or HRV) is based on a mathematical analysis of a series of consecutive heart actions - the so-called NN intervals.
RMSSD “Root Mean Square of Successive Differences” is one of the most important parameters that provides information about the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. It describes the short-term variability of the heartbeat, how strongly the heart rate changes from one heartbeat to the next. Calculation of the RMSSD value: The time difference between successive RR intervals is multiplied by itself in order to obtain only positive values. These intermediate values are summed and divided by the number of RR interval differences to obtain the mean value. The square root is taken from the mean of these squared differences. The RMSSD is often referred to as the value for the body's ability to recover or as the “brake” of the nervous system. The higher this number is, the better.

